Botanical Name: Myristica Fragrans Common name: Nutmeg Plant fa Read More
|
Botanical Name: |
Myristica
Fragrans |
|
Common name: |
Nutmeg |
|
Plant
family: |
Myristicaceae |
|
Genus: |
Myristica |
|
Appearance/Color: |
Colorless to slight yellow color liquid having clear and thin consistency |
|
Odor: |
It has
a sweet, spicy scent reminiscent of nutmeg with medium aroma at middle note |
|
Blends With: |
Lavender, Bay, Orange, Geranium, Clary Sage, Rosemary, Lime,
Petitgrain, Mandarin and Coriander |
|
Origin: |
Sri
Lanka |
|
Source: |
Aril (pericarp) which surrounds the ripe seed |
|
Method
of Extraction: |
Steam
Distillation |
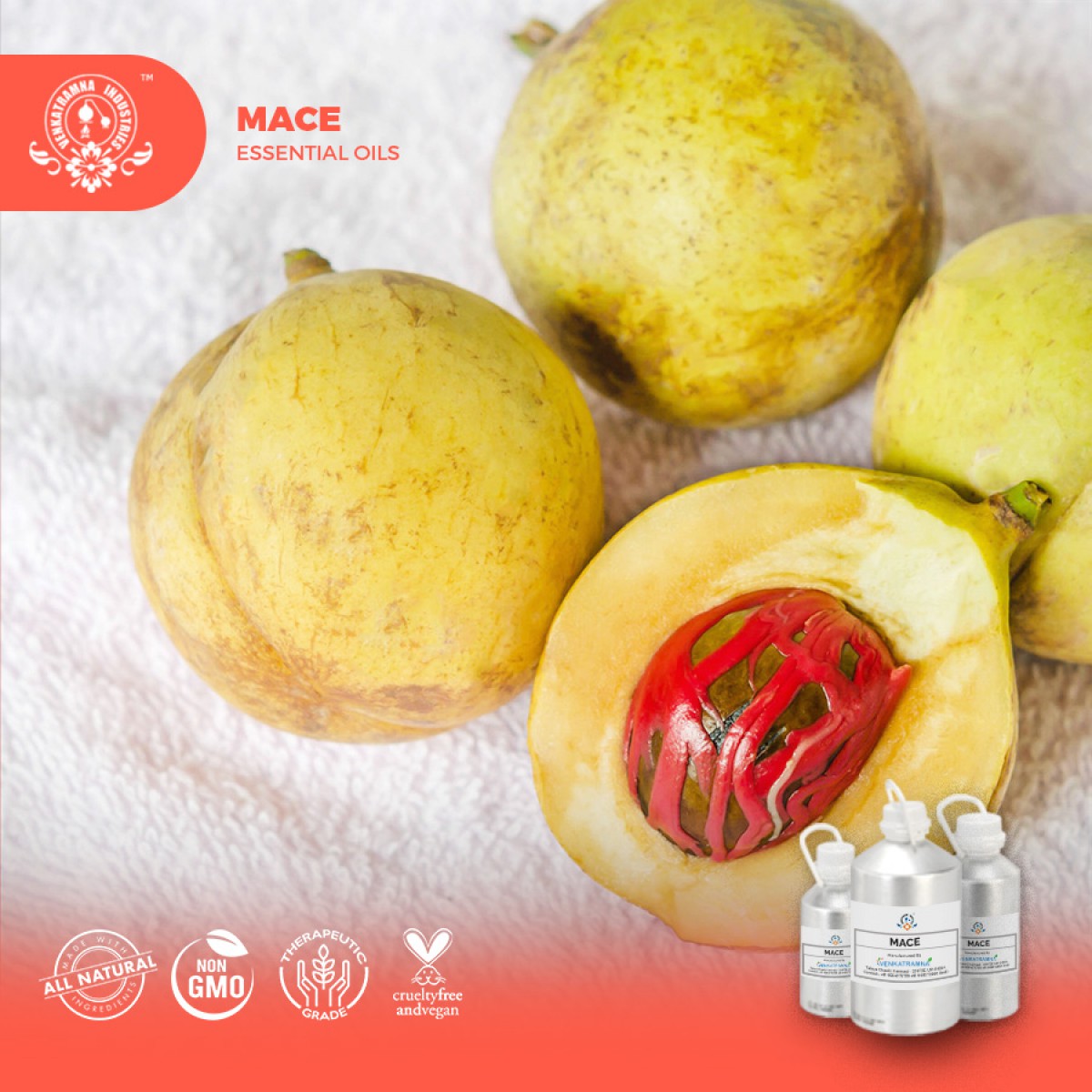
Myristica fragrans is
commonly named nutmeg or mace. It is an aromatic evergreen tree with spreading
branches and a yellow fleshy fruit similar in appearance to an apricot or
peach. The nutmeg fruit is pendulous and
similar in presentation to a peach. When fully mature, it splits in two, exposing
a crimson-colored aril. This is the mace which surrounds the nutmeg pit. Mace
is a vibrant red-colored seed husk covering (aril).
Myristica fragrans is a small evergreen tree, usually 5–13 m (16–43 ft) tall, but occasionally reaching 20 m (66 ft). The alternately arranged leaves are dark green, 5–15 cm (2.0–5.9 in) long by 2–7 cm (0.8–2.8 in) wide with petioles about 1 cm (0.4 in) long.
DISCLAIMER
The complete range of conditions
or methods of use are beyond our control therefore we do not assume any
responsibility and expressly disclaim any liability for any use of this
product. Information contained herein is believed to be true and accurate however,
all statements or suggestions are made without warranty, expressed or implied,
regarding accuracy of the information, the hazards connected with the use of
the material or the results to be obtained from the use thereof. Compliance
with all applicable federal, state, and local laws and local regulations
remains the responsibility of the user.
The FDA has not evaluated the
statements on this website. No claims are made by Venkatramna Industries as to
the medicinal value of any products from vriaroma.com or by us. The information
presented here is for educating our customers about the traditional uses of
essential oils and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any
disease. You are responsible for understanding the safe application of these products.
If you have any questions, please call or email us for further information.
As per NAHA guidelines, New Directions Aromatics
(NDA) does not recommend the ingestion of essential oils. It is imperative to
consult a medical practitioner before using Essential Oils for therapeutic
purposes. Pregnant and nursing women and those taking prescription drugs are
especially advised not to use this product without the medical advice of a
physician. The oil should always be stored in an area that is inaccessible to
children, especially those under the age of 7.
Mace Essential Oil has a history of medical
use in combination with nutmeg. It has progressed over time and is added to
soaps, perfumes and it is also used as a cooking ingredient. It smells like and
is very close to nutmeg in its makeup. Its analgesic properties also make it
useful for treating muscle fatigue and arthritis.
The essential oil derived from
Mace is the most efficacious. The oil is a potent brain booster. It increases
concentration and relieves stress. Mace is an excellent liver tonic. It
dissolves kidney stones and prevents infection. The herb is also beneficial for
the heart as it stimulates blood circulation. Mace’s anti-inflammatory
properties are used to treat joint and muscle aches.
The seed of nutmeg is rich in
essential oils. It is a bitter, astringent, spicy herb that acts as a warming,
digestive tonic. It controls vomiting and relaxes spasms. When applied
externally, it has an antiinflammatory effect. Nutmeg is also said to have
stimulant, carminative and aphrodisiac properties. The seed is taken internally
in the treatment of diarrhoea, dysentery, vomiting, abdominal distension,
indigestion and colic. Externally, the seed is used to treat toothache,
rheumatic and abdominal pains (including labour pains). Some caution is advised
- taken in excess the seed can cause severe headache, nausea, dizziness and
delirium. The seed is used in Ayurveda to treat poor digestion, insomnia,
urinary incontinence and premature ejaculation.
Nutmeg contains 25–30% fixed oils
and 5–15% volatile oils (camphrene, eugenol, etc.), and also other molecules
such as myristic acid, myristicin, and lignin compounds. Among these molecules,
eugenol is widely used in dentistry, and is very effective in antibacterial
activity against oral bacteria. Nutmeg essence is mostly used to alter spicy
notes. It is sometimes added to eaux de Colognes and eaux de toilettes for men.
Used as a flavor enhancer in mashed potatoes, soups, baked or cooked dishes,
candies, chewing gum, beverages and breakfast cereal.
COMMON
USAGE
·
Analgesic
·
Anti-rheumatic
·
Antiseptic
·
Anti-spasmodic
·
Carminative
·
Digestive
·
Laxative
·
Stimulant
and tonic
·
Stimulate
appetite
·
Assisting
the reproductive system
Ingredients:
|
S.No |
Key Constituents |
Strength (%) |
|
1 |
b-Pineneþsabinene |
45.5 |
|
2 |
a-Pinene |
15.2 |
|
3 |
1,8-Cineoleþ(þ)-limonene |
7.0 |
|
4 |
Myristicin |
5.9 |
|
5 |
Terpinen-4-ol |
4.5 |
|
6 |
a-Terpineneþp-cymene |
3.5 |
|
7 |
a-Phellandrene |
3.2 |
|
8 |
Elemicin |
3.1 |
Safety Summary
·
Hazards:
Potentially carcinogenic, based on safrole and methyleugenol content; may be
psychotropic.
·
Respiratory sensitization: Breathing high
concentrations of vapor may cause anesthetic effects.
Safety
advice
Recommended maximum dermal use of 2% for the
Sri Lankan oil and a maximum oral dose of 73 mg based on 1.9% safrole and 0.2%
methyleugenol content, and a dermal maximum of 4.1% and a maximum oral dose of
146 mg for the Sri Lankan oil based on 0.7% safrole and 0.2% methyleugenol.
These are based on dermal limits of 0.05% and 0.02%, and oral dose limits of
0.025 and 0.01 mg/kg for safrole and methyleugenol, respectively.
Organ Specific Effects
·
Adverse skin reaction: Undiluted mace oil was moderately irritating
to rabbits, but was not irritating to mice or pigs; tested at 8% on 25
volunteers it was neither irritating nor sensitizing. It is non-phototoxic.
·
Neurotoxicity: Psychotropic effects have been reported for
nutmeg in high doses. Myristicin and elemicin are thought to be responsible,
but other synergistic elements may need to be present for a psychotropic effect
to take place.
Systemic
Effects
·
Acute
Toxicity: Mace oil acute
oral LD50 in rats 3.64 g/kg; acute dermal LD50 in rabbits >5 g/kg.
·
Carcinogenic/anti carcinogenic potential: No data was found for mace oil. Safrole and
methyleugenol are carcinogenic if the dose is sufficiently high; (þ)-limonene
and myristicin display anticarcinogenic activity.
Toxicity
·
Acute fish toxicity (LC50 / 96 HOUR) – No
data available
·
Toxicity to aquatic plants – No data
available
·
Toxicity to microorganisms – No data
available
·
Toxicity threshold – No data available
·
Persistence and degradability Biodegradation is
expected
·
Bio-accumulative potential Bioaccumulation is
unlikely
Avoid exposure to marine environments and waterways.




 MSDS-Mace.pdf
MSDS-Mace.pdf




